Here comes the sun: Solar power faces challenges
Published 8:00 am Wednesday, July 19, 2017
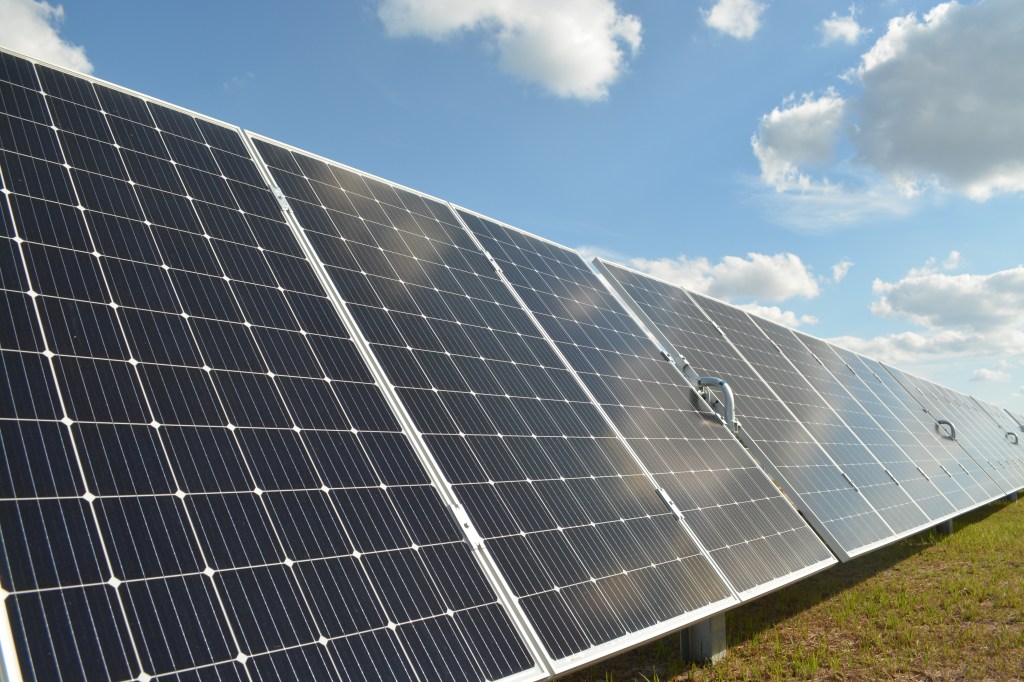

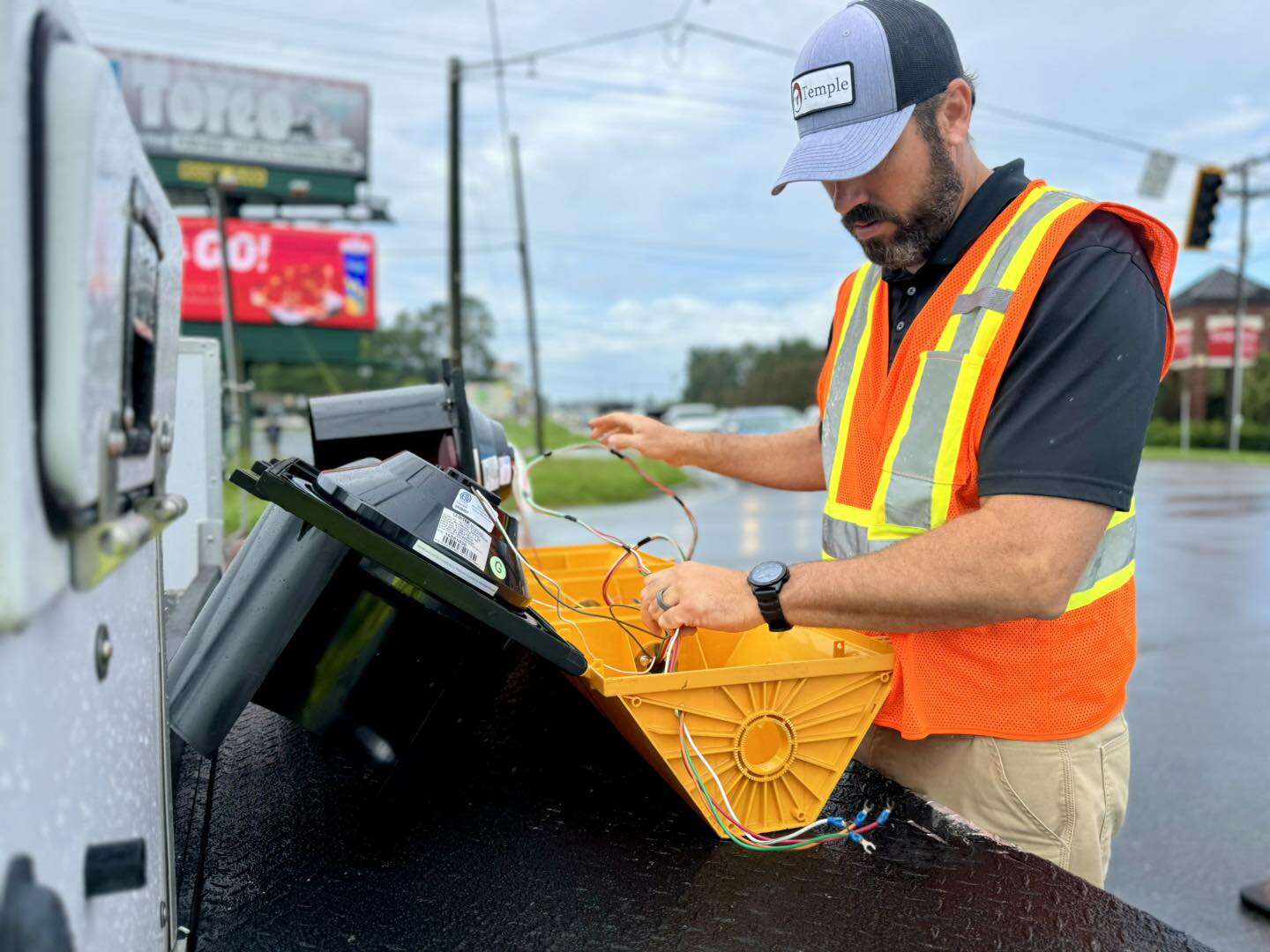
- Solar panels on Seminole Electric’s solar farm which the company uses for its Cooperative Solar program that includes Suwannee Valley Electric.
LIVE OAK — Few things are as certain as the sun rising every morning in the east and setting every evening in the west.
The certainty is alluring. If a tiny seed can capture the energy of the sun to grow into a massive tree, then surely people can use it to power a standard 100 watt light bulb.
Solar energy was once considered to be the stuff of science fiction or futuristic thinkers. Burning coal and fossil fuels, building dams and and even nuclear reactors to produce energy were all considered viable sources of power generation. But solar power generation is here and here to stay.
Still, like most things, there is a catch.
The Sunlight Project team in Georgia and North Florida took a look into one of the world’s fastest growing markets.
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, Florida has almost 500 solar companies at work that have invested nearly $1.5 billion into solar power ($523.6 million in 2016 alone), solar energy can no longer be ignored or seen as a niche. Georgia, meanwhile, has 236 solar companies with more than $2 billion invested into solar, $1.2 billion last year.
And SEIA data shows that Florida produces about 725 megawatts of power, while Georgia produces about twice that amount or close to double the amount of a typical coal plant. The Peach State also has 167,000 homes powered by solar and nearly 4,000 solar-related jobs to the Sunshine State’s 79,000 solar-powered homes and more than 8,000 solar jobs.
Clearly, it’s not just eco-friendly people jumping on the solar-power bandwagon.
Amanda and Corey Reed in Mayo, Fla., just wanted to find a way to reduce the cost of their electric bill.
As poultry farmers, they often receive bills upwards of $3,000.
“A third of our annual income was spent on energy consumption,” Amanda Reed said.
Reed said she had been looking into solar power for several years but it was so expensive to get started. She knew there were programs for certain farmers to get financial help to use solar power but there was nothing for poultry farmers.
“The cost of production was killing us,” Reed said.
Three years ago, Reed reached out to the Florida Department of Agriculture, Department of Energy, Congressman Ted Yoho and Representative Halsey Beshears to find options.
Reed’s hard work and persistence paid off.
The poultry farm is now part of a pilot program for the Department of Agriculture to see if solar power is a viable option for poultry farmers.
“We are the guinea pigs,” Reed said.
Solar panels that supply the farm with approximately half of its annual energy were installed at the farm. As part of the program, Reed will collect data for a year and compare it to the previous year to show how much the farm saved with solar power.
They turned on the solar panels in February and the savings have been tremendous, she said.
“Our bill last month was $25 compared to last year’s $1,200 bill,” Reed said.
The $25 was the cost of using Suwannee Valley Electric Cooperation’s meter, not energy consumption. Reed said the pilot program is going phenomenally.
She believes solar power is the future for farmers. The cost of production is forcing many farms out of business and solar power could be a way to save farming and agriculture.
Once a year, data is collected, and Reed and the Department of Agriculture plan to present it to the state. They hope to get a grant or cost-sharing program started for other poultry farmers.
Across the SunLight Project coverage area — Live Oak, Jasper and Mayo, Fla., and Valdosta, Dalton, Thomasville, Milledgeville, Tifton and Moultrie, Ga., along with the surrounding counties — there are a number of programs available for residents to capture the power of the sun without spending an arm and a leg to install solar panels to the roof of their home.
Power companies and solar
The Reeds, for example, are part of the 33 SVEC members that have solar panels connected to the SVEC system, or what the co-op calls member-owned solar.
Through the program, SVEC allows members to generate power for their use. Using net metering, SVEC compares the amount of power it provides to the amount the member provides the co-op. In months when the member’s solar power system provides more energy than the member uses, SVEC credits the excess power.
The credits are carried over to the next month’s bill. At the end of a year, the credit can be paid out with the tariff to the member or, if the member desires, SVEC will credit the dollar amount to the next year’s first billing.
Seminole Electric Cooperative, which provides power to SVEC and eight other co-ops, and the nine not-for-profit co-ops are also looking into providing cooperative solar.
According to Ryan Hart, Seminole’s manager of corporate communication and energy policy, the large-scale solar project is a result of cooperatives listening to their members and taking action.
Construction began on the solar plant in August 2016, When the program is ready to begin energy output from the facility, it will be allotted to the member cooperatives. The cooperatives will then have the choice to add the power to their energy portfolio or sell individual units to their member consumers.
SVEC was allotted 144 solar blocks from the project. The blocks sold out within four hours, according to SVEC’s Jon Little, who said members were allowed to purchase two blocks.
For some Georgia electric membership corporations, not-for-profit consumer-owned electric distribution systems, customers have an option for purchasing green energy, but it is not available for Colquitt EMC customers.
The company purchases electricity generated at solar facilities and is part of a group using power generated by burning waste gas from the landfill in Lowndes County, said Charlie Tucker, Colquitt EMC’s manager of engineering.
Green Power EMC, a cooperative of participating Georgia EMCs created in 2001, has a 52-megawatt solar farm near Hazelhurst with 630,000 solar panels covering 480 acres on a 942-acre site. It began operating last year and has a generating capacity to power about 8,500 households.
A second 89,000-panel array covering half of a 270-acre site provides enough energy for about 3,000 homes.
“We’re just putting solar directly into our mix,” Tucker said. “It has gotten a lot more competitive over the last couple of years.”
Colquitt EMC will consult with consumers looking to install residential panels.
“We’re more involved in the safety aspects of getting (the excess generation) back on line,” he said.
Colquitt EMC purchases that excess energy generated beyond a resident’s own use. Tucker estimated that less than 2 percent of the power it sells comes from purchasing solar and its landfill gas project.
EMC members in the county are not exactly banging down the door at this point.
“We haven’t had a lot of interest in this part of the state,” Tucker said. “We probably get a couple of calls a month about it.”
He estimated there are about 14 customers who are selling power back to the EMC. He said there are others with solar installations who are using the electricity generated but not producing any extra to sell but he had no estimate of how many customers fall into that category.
Problems with solar programs
James LaValley, a Valdosta, Ga., resident, wanted to invest in his home — not for himself but for his children. In 2015, the 74-year-old retired New Yorker decided he would go solar. After a quick internet search, he found a business in Vidalia, known more for its onions than solar power, that would come to his place in Valdosta to install solar panels to his roof.
“The way this guy put it seemed to me like a no-brainer,” LaValley said. “Looked to me like I wouldn’t be paying any energy bill at all.”
Installation took two weeks. It cost LaValley $30,000, but with federal tax breaks, he only ended up $20,000 in the hole. The cost didn’t bother him. It was worth the investment, he thought and he said he was told his investment would be paid back in less than five years.
The useful life of a solar panel is estimated at 20 to 30 years.
LaValley didn’t see a downside. He believed his energy bill would go from $170 a month to as low as $15, maybe $10. After the panels were up and running, he became excited when he saw they were producing more energy than his house was using.
“It was great. I thought my bill would go even lower,” LaValley said. “I was happy, then I saw the actual bill and it was like I was struck in the heart.”
His bill went down but not by as much as he wanted it to — as he needed it to. When LaValley brought this up to the installer, who was also a lawyer, he told LaValley it was normal and this was a battle he had been fighting in court for years.
“I felt ripped off, like I had been taken advantage of,” LaValley said.
His solar panels were still producing way more energy than he was using but his energy wasn’t worth as much as he was told it would be. His next step was to find a local professional to manage his solar panels.
LaValley turned to Ron Jackson, project manager of South Georgia Solar Power. Jackson said solar power has benefited the utility companies at the expense of homeowners who have high-cost panels installed.
He said people such as LaValley invest their own money, feeding the energy into a utility provider’s grid only to be compensated a fraction of the amount utility companies charge for the same power.
Energy that LaValley sells to a utility company such as Georgia Power is purchased for less than the cost of the energy Georgia Power sells back to LaValley.
For example, Georgia Power can buy any power LaValley doesn’t use for five cents per unit and sell it back to him at 15 cents.
“He is making energy for them and not seeing any benefit,” Jackson said. “He should be getting $20 a month from them not a bill.”
The problem in LaValley’s situation has to do with energy storage. He is producing too much energy and has nowhere to put it except into Georgia Power’s grid. He could buy a Tesla Powerwall, a giant battery meant for storing solar energy, but those can cost about $5,000.
For LaValley, that’s more money then he bargained for, and the situation he is in is why Georgia Power, the largest subsidiary of Southern Company, one of the nation’s largest generators of electricity, recommends for people to speak to them before investing in solar power.
John Kraft, Georgia Power representative, said the company is aware of situations such as LaValley’s. The company offers tremendous help to those interested in solar, he said. Georgia Power will work with them and even send representatives to their home to look into the matter.
“What we’re really doing is trying to find out why they want solar,” Kraft said. “There can be a number of reasons, like for the environment or for a cheaper electric bill. Sometimes we have to tell them that there are cheaper ways to lower your electric bill than installing solar panels.”
Kraft said he sees a lot of customers thinking they can install solar panels and never pay an electric bill again. However, unless someone has a place to put the power, they will continue paying power bills.
The person will have to sell their unused power back to a utility company and buy back power during times when the panels aren’t generating power, at night or early in the morning, for instance.
The utility company offers to pay the producer only as much as it costs to produce solar power. If a utility company can produce solar energy at a solar farm for 5 cents per unit, it isn’t going to pay a residential producer a higher rate for energy it doesn’t need.
From LaValley’s point of view, this isn’t fair.
He is producing Georgia Power energy and thinks he is not getting a fair rate. However, why should Georgia Power pay him more for something it already produces for less?
Regulating the Sun
Thomas County commissioners broached the idea of solar-panel legislation last year. In October, they approved a 30-day moratorium on solar installations that in November was extended to six months.
The county lifted the moratorium in late April, two weeks ahead of its scheduled end. Commissioners have put in place a $1,000 zoning application fee for solar facilities.
Earlier this year, commissioners approved an amendment that split solar use into two categories — one for installations at homes and businesses that would provide power to locations and another for solar farms that would generate power to be sold to utility companies.
Solar farms of more than 200 acres would be considered commercial ventures and permitted in industrial and commercial land use districts and as conditional use in agricultural districts. They would not be permitted in residential zones.
Solar farms of 200 acres or fewer will be classified as a conditional use in agricultural districts and subject to approval on a case-by-case basis. Setbacks for the location of solar facilities are 100 feet from all property lines, with 500-foot setbacks from residences and residential land use districts.
Another provision requires applicants for solar facilities to provide a performance guarantee in the form of a bond, irrevocable letter of credit or other financial security acceptable to Thomas County in the amount of 125 percent of the estimated decommissioning cost, minus the salvageable value, or $50,000, whichever is greater.
Thomas County Commission Chairman Ken Hickey said additional tweaks to legislation might be needed, including a consideration of necessary variances for installers.
“With the solar ordinance, I’ve said all the time, there is no one size fits all. All the land is different. The contours are different. The acreage is different. The topography is different. Everything is different. You need this kind of variance so you can work with people on their projects. Whether you choose to or not, the option will be there,” he said.
Grady County also enacted moratoriums while discussing potential solar facilities.
“One prospective solar farm developer had plans for a very large solar farm that could have large impacts on the county,” Grady County Administrator Carlos Tobar said of the moratoriums. “I wanted to make sure the board of commissioners was aware of such a large development. They all agreed that they should address such a project with an ordinance.”
The first moratorium, 60-days long, was enacted in February and the second brief moratorium was enacted in May. The Grady County Commission approved an ordinance for solar farms, which falls under the county’s land use regulations, in early June.
Grady’s land use ordinances, now including solar farms, require an opaque vegetative buffer along all property lines. Setbacks include 35 feet from all property lines and 300 feet from homes, churches or businesses. The ordinance also includes decommissioning specifics for the solar facility owner if the facility discontinues operation.
“We certainly know from our neighboring counties that solar farms generate significant tax revenue for a community,” Tobar said. “That reduces the tax burden on our property owners and that is a great thing.”
One solar farm is under construction in Grady County — small enough that the previous administration did not address it legislatively, Tobar said.
Colquitt County has approved three solar projects so far this year. The first was a 10-acre Hannah Solar project. Hannah Solar is a North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners certified solar power company. The site produces 2 megawatts and is up and running, said Justin Cox, director of the county’s compliance office
The county faced an influx of permit requests near the deadline for bids to Georgia Power. Commissioners enacted a 90-day moratorium while it studied the issue and drafted a solar ordinance.
Since the moratorium was lifted, two potential projects have been permitted, Cox said. One is a large 95.9-megawatt development covering 420 acres on eight parcels of land issued to eagle Solar in May.
The other, permitted in April to Odom Solar, would have 260 acres of panels producing 20 megawatts.
Both were among the contract bids to Georgia Power.
“Both had special-use permits granted,” Cox said. “Whether they’re going to proceed with them, that’s unknown.”
Two other companies have requested permit documents.
“They’ve got the paperwork but they haven’t turned anything in,” Cox said.
The City of Valdosta has no local ordinances that directly regulate the use of solar power, said Sementha Mathews, the city public information officer.
From a zoning standpoint, the city simply looks at the use of solar arrays in one of two different categories: “individual use” to augment a particular development, or “solar farm” for the primary purpose of generating electricity to be sold back to the grid.
If a solar panel is attached to a building, the city considers it part of the building. If a solar panel is freestanding, it is considered the same as any other freestanding accessory structure. If it is a solar electric generating facility, it is treated similarly to other such electric-generating facilities.
“The City of Valdosta is leading the state and this part of the country with their commitment to renewable energy resources,” Mathews said.
Sites located within the city limits or on city-owned property are 11 acres of land for Mud Creek Wastewater Treatment Plant; five acres for New Withlacoochee Wastewater Treatment Plant; eight acres at a closed landfill located on Val Tech Road, adjacent to the Valdosta State Prison, along with another 3.5 acres near the shooting range on Val Tech Road.
In the City of Valdosta, sites for solar panels are chosen when the lands no longer have a public use, such as an old landfill.
“The use of Solar PD installations is an innovative way for the City of Valdosta to be in the renewable energy game and also generate capital assets off of land that could not be developed for anything else,” Mathews said.
As for Lowndes County, officials said they are supportive of solar energy but the county does not have an active solar power generation program, said Paige Dukes, county clerk. Lowndes County also does not have any laws discouraging or incentivizing solar power.
Who Is Using Solar Power?
While Seminole and SVEC are looking to add solar power as a source of energy for their member consumers, Duke Energy is looking to Suwannee County as a source of solar power. The company retired the Suwannee River Power Plant in December after 63 years of service.
In January, Duke announced plans for an 8.8-megawatt solar plant to be built on 70 acres of land just east of the existing plant. The Suwannee Solar Facility, which Duke hopes to have in operation by the end of the year, will be able to power about 1,700 average homes at peak production.
The Suwannee solar plant will be Duke’s third as the company has already constructed plants in Osceola County and Taylor County.
“We are committed to expanding clean energy in Florida,” said Harry Sideris, Duke Energy state president – Florida. “Retiring older units like those at Suwannee River and building new solar power plants provides the greatest amount of renewable energy for customers, in the most economical way.”
Georgia Power has also been looking to boost sun-based generation.
Spokesman John Kraft said the company has made a huge commitment to renewable energy, looking to boost capacity through a mix of solar, wind and biomass by some 1,200 megawatts through its Renewable Energy Development Initiative. This included a bidding process for 525 megawatts that ended earlier this year and an equal amount to be bid in 2019. Of the total of 1,050 megawatts, up to 300 are expected to be generated by wind.
“We have one of the biggest voluntary solar expansions in the nation,” Kraft said.
He contrasted this voluntary expansion to some states that mandated rapid ramping up of solar earlier, which locked in higher costs before technology improved and cost of production dropped. Currently, the company’s mix includes about 4 percent renewable sources, including hydroelectric, solar and other renewables. About 47 percent is generated with natural gas, 29 percent with coal, and 20 percent nuclear.
Kraft said hydro and other renewables represent 8 percent of total capacity, but solar energy is limited in that it is only made while the sun shines. Georgia Power is diversifying its renewable energy source by buying 250 megawatts of wind power generated in Oklahoma.
Georgia Power’s parent company Southern Company has a research project in Northwest Georgia involving storing power generated through solar for later use with the Electric Power Research Institute. Georgia Power also has a small research project on the roof of its headquarter’s parking facility, where various types of solar panels are tested.
“Here in the Southeast, we get a lot of cloud cover, a lot of rain and humidity,” Kraft said. “We’re looking at which panels work best in the Southeast. That’s an ongoing project.”
In this environment, the best solar generation is realized in the spring and fall when humidity drops, he said.
“Solar panels are most efficient when it’s cool,” Kraft said.
Installing Panels at Home
While renting a panel block from an existing solar farm is relatively inexpensive, installing a power system for one’s home can cost many thousands of dollars.
Even with numerous loans, tax credits and incentives, including the federal Investment Tax Credit that returns up to 30 percent of the cost of a system, the average homeowner will need to operate the system for several years before seeing a return on the investment, industry representatives have said.
For residences and businesses looking to purchase sun power, Georgia Power offers its Simple Solar program where customers pay an extra penny per kilowatt hour per month. The program replaced the Green Energy program, which was discontinued at the end of 2016.
Later this year, Georgia Power will introduce its community solar program, where customers can purchase off-site solar panels maintained by the company. Customers will receive the benefit of the power generated by the panels.
Georgia Power also gives extensive advice to homeowners looking to install rooftop-solar on their homes, said Kraft. That includes a representative meeting with the homeowner to discuss a project through installation, if the customer chooses.
The advice covers such aspects as the practicality — a mostly shaded roof would not be a good candidate for an expensive solar installation. Other considerations include the age of the roof; installing solar panels on a roof that is likely to need replacing in a few years could be a poor choice, Kraft said.
In some instances, the advice may be to replace an old central air system with a newer, more efficient one, where the project could pay for itself in less than five years versus 12 years for solar, he said.
Putting solar panels on a house should be seen as a serious investment and not as a quick way to reduce a power bill, experts said.
For homeowners only motivated by a desire to reduce monthly energy costs, going solar is not a quick answer — yet.
The SunLight Project team of journalists who contributed to this report includes Jessie R. Box, Patti Dozier, Thomas Lynn, Charles Oliver, Will Woolever, Alan Mauldin and Eve Guevara, along with the writer, team leader John Stephen. To contact the team, email sunlightproject@gaflnews.com.